Free Online Materials For Those Students Who Need Substitute Classes For Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics !
Friday, June 28, 2024
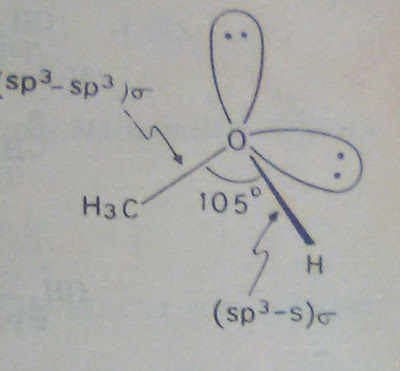
Atomic Structure
Wednesday, December 29, 2021
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
The study of chemistry is very important as its domain encompasses every sphere of life. Chemists study the properties and structure of substances and the changes undergone by them. All substances contain matter, which can exist in three states – solid, liquid or gas. The constituent particles are held in different ways in these states of matter and they exhibit their characteristic properties.
Classification of Matter
Matter can also be classified into elements, compounds or mixtures. An element contains particles of only one type, which may be atoms or molecules. The compounds are formed where atoms of two or more elements combine in a fixed ratio to each other. Mixtures occur widely and many of the substances present around us are mixtures.
When the properties of a substance are studied, measurement is inherent.
Measurements of Substances in SI System
The quantification of properties requires a system of measurement and units in which the quantities are to be expressed. Many systems of measurement exist, of which the English and the Metric Systems are widely used. The scientific community, however, has agreed to have a uniform and common system throughout the world, which is abbreviated as SI units (International System of Units).
Since measurements involve recording of data, which are always associated with a certain amount of uncertainty, the proper handling of data obtained by measuring the quantities is very important. The measurements of quantities in chemistry are spread over a wide range of 10-31 to 1023. Hence, a convenient system of expressing the numbers in scientific notation is used. The uncertainty is taken care of by specifying the number of significant figures, in which the observations are reported. The dimensional analysis helps to express the measured quantities in different systems of units. Hence, it is possible to interconvert the results from one system of units to another.
Basic Laws of Chemical Combination
The combination of different atoms is governed by basic laws of chemical combination — these being the
1. Law of Conservation of Mass, 2. Law of Definite Proportions, 3. Law of Multiple Proportions,
4. Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes and 5. Avogadro Law.
All these laws led to the Dalton’s atomic theory, which states that atoms are building blocks of matter.
Atomic and Molecular Mass
The atomic mass of an element is expressed relative to 12C isotope of carbon, which has an exact value of 12u. Usually, the atomic mass used for an element is the average atomic mass obtained by taking into account the natural abundance of different isotopes of that element. The molecular mass of a molecule is obtained by taking sum of the atomic masses of different atoms present in a molecule. The molecular formula can be calculated by determining the mass per cent of different elements present in a compound and its molecular mass.
Avogadro Number
The number of atoms, molecules or any other particles present in a given system are expressed in the terms of Avogadro constant (6.022 × 1023). This is known as 1 mol of the respective particles or entities.
Stoichiometric Calculations
Chemical reactions represent the chemical changes undergone by different elements and compounds. A balanced chemical equation provides a lot of information. The coefficients indicate the molar ratios and the respective number of particles taking part in a particular reaction. The quantitative study of the reactants required or the products formed is called stoichiometry. Using stoichiometric calculations, the amount of one or more reactant(s) required to produce a particular amount of product can be determined .
The Amount of Substance in a Solution
The amount of substance present in a given volume of a solution is expressed in number of ways, e.g., 1. Mass Per cent, 2. Mole fraction, 3. Molarity and 4. Molality.
Saturday, May 23, 2020
2. Acids, Bases, and Salts Class X
Monday, April 20, 2020
1. रासायनिक अभिक्रियाएँ एवं समीकरण
अध्याय 1
रासायनिक अभिक्रियाएँ एवं समीकरण
प्रश्नोत्तर NCERT Textbook
1.1 रासायनिक समीकरण
प्रश्न1. वायु मे जलाने से पहले मैग्नीशियम रिबन को साफ क्यों किया जाता है?
उतरः
मैग्नीशियम एक अति क्रियाशील धातू है अतः यह हवा के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करके मैग्नीशियम ऑक्साइड का एक परत बनाता है जो आगे कि प्रतिक्रिया को जारी रखने में बाधा पहुँचाता है। इसलिए, वायु अथवा ऑक्सीजन में जलाने से पहले मैग्नीशियम रिबन को रेगमाल(Sand Paper) से रगडकर साफ कर लिया जाता है।
प्रश्न2. निम्नलिखित रासायनिक अभिक्रियाओॆ के लिए संतुलित समीकरण लिखिएः
(i) हाइड्रोजन + क्लोरीन → हाइड्रोजन क्लोराइड
उतरः
H₂ + Cl₂ → 2HCl
(ii) बेरियम क्लोराइड + ऐलुमीनियम सल्फेट → बेरियम सल्फेट + ऐलुमिनियम क्लोराइड
उतरः
(iii) सोडियम + जल → सोडियम हाइड्रोक्साइड + हाड्रोजन
उतरः
2Na + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + H₂
प्रश्न 3. निम्नलिखित अभिक्रियाओं के लिए उनकी अवस्था के संकेतो के साथ संतुलित रासायनिक समीकरण लिखिएः
(i) जल में बेरियम क्लोराइड तथा सोडियम सल्फेट के विलयन अभिक्रिया करके सोडियम क्लोराइड का विलयन तथा अघुलनशील बेरियम सल्फेट का अवक्षेप बनाते हैं।
उतरः
BaCl₂(aq) + Na₂SO₄(s) → BaSO₄(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
(ii) सोडियम हाइड्रोक्साइड का विलयन (जल में) हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल के विलयन (जल में) से अभिक्रिया करके सोडियम क्लोराइड का विलयन तथा जल बनाते है।
उतरः
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l)
1.2 रासायनिक अभिक्रियाओं के प्रकार
प्रश्न1. किसी पदार्थ X के विलयन का उपयोग सफेदी करने के लिए होता है।
(i) पदार्थ X का नाम तथा इसको सूत्र लिखिए।
उतरः
कैल्सियम ऑक्साइड अथवा बिना बुझा हुआ चूना
रासायनिक सूत्रः (CaO)
(ii) ऊपर (i) में लिखे पदर्थ X की जल के साथ अभिक्रिया लिखिए।
उतरः
CaO एवं H₂O की रासायनिक अभिक्रिया नीचे दिया गया है।
CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂(aq) + ऊष्मा
प्रश्न 2. क्रियाकलाप 1.7 में एक परखनली में एकत्रित गैस की मात्रा दूसरी से दोगुनी क्यो? उस गैस का नाम बताइए।
उतरः
वियोजन अभिक्रिया के कारण परखनली में एकत्रित गैस हाइड्रोजन का आयतन ऑक्सीजन से से दोगुनी है।
1.2.3 विस्थापन अभिक्रिया
प्रश्न1. जब लोहे की कील को कॉपर सल्फेट के विलयन में डुबोया जाता है तो विलयन का रंग क्यो बदल जाता है?
उतरः
इस अभिक्रिया में, लोहे ने कॉपर को कॉपर सल्फेट के विलयन से विस्थापित कर दिया। इस कारण विलयन के रंग के साथ-साथ लोहे के कील का भी रंग बदल जाता है।
इस अभिक्रिया को विस्थापन अभिक्रिया कहा जाता है।
ऱासायनिक अभिक्रिया को नीचे दिखाया गया है।
Fe(s) + CuSO₄(aq) → FeSO₄(aq) + Cu(s)
प्रश्न 2. क्रियाकलाप 1.10 से भिन्न द्विविस्थापन अभिक्रिया का एक उदाहरण दीजिए।
उतरः
द्विविस्थापन अभिक्रिया का उदाहरण नीचे दिया गया है।
Na₂SO₄(aq) + BaCl₂ → BaSO₄(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
प्रश्न 3. निम्न अभिक्रियाओं में उपचयित पदार्थ की पहचान कीजिएः
(i) 4Na(s) + O₂ → 2Na₂O(s)
उतरः
इस अभिक्रिया में सोडियम उपचयित पदार्थ है।
(ii) CuO(s) + H₂(g) → Cu(s) + H₂O(l)
उतरः
इस अभिक्रिया में हाइड्रोजन उपचयित पदार्थ है।
अभ्यास
प्रश्न 1. नीचे दी गयी अभिक्रिया के संबंध मे कौन सा कथन सत्य है?
2PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb(s) + CO₂(g)
(a) सीसा अपचयित हो रहा है।
(b) कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड उपचयित हो रहा है।
(c) कार्बन उपचयित हो रहा है।
(d) लेड ऑक्साइड अपचयित हो रहा है।
(i) (a) एवं (b)
(ii) (a) एवं (c)
(iii) (a), (b) एवं (c)
(iv) सभी
उतरः
सीसा अपचयित हो रहा है एवं कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड उपचयित हो रहा है।
अतः सही विकल्प (ii) होगा।
प्रश्न2. Fe₂O₃ + 2Al →Al₂O₃ + 2Fe
उपर दी गयी अभिक्रिया किस प्रकार की हैः
(a) संयोजन अभिक्रिया
(b) द्विविस्थापन अभिक्रिया
(c) वियोजन अभिक्रिया
(d) विस्थापन अभिक्रिया
उतरः
यह एक प्रकार का विस्थापन अभिक्रिया है क्योंकि अल्युमिनियम, लोहे को उनके योगिक से विस्थापित कर रहा है।
अतः सही विकल्प (d) होगा।
प्रश्न 3. लौह चूर्ण पर तनु हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल डालने से क्या होता है? सही उत्तर पर निशान लगाइए।
(a) हाइड्रोजन गैस एवं आयरन क्लोराइड बनता है।
(b) क्लोरीन गैस एवं आयरन हाइड्रॉक्साइड बनता है।
(c) कोई अभिक्रिया नही होती है।
(d) आयरन लवण एवं जल बनता है।
उत्तरः
हाइड्रोजन गैस एवं आयरन क्लोराइड बनता है।
1.Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chapter 1.
Chemical Reactions and Equations
Questions Answers (NCERT Textbook)
1.1 Chemical Equations
Q.No.1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air ?
Answer:
Magnesium ribbon is very reactive metal so it easily reacts with air and make a layer of magnesium oxide. The layer of magnesium oxide is quite stable and prevents further reaction of magnesium with air or oxygen. Therefore, magnesium ribbon is cleaned by sand paper to remove the layer of magnesium oxide before burning in air. Magnesium ribbon burns with air and gives magnesium oxide.
The word equation for the reaction would be
Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide.
This word equation may be represented by following chemical equation.
2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
Q.No.2. Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
(i) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
Answer:
The above word equation may be represented by following chemical equation
H₂ + Cl₂ → 2HCl
(ii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
Answer:
The above word equation may be represented by
3BaCl₂ + Al₂(SO₄)₃ → 3BaSO₄ + 2AlCl₃
(iii) Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Oxygen
Answer:
The above word equation may be represented by following chemical equation.
2Na + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + H₂
Q.No.3. Write a balanced chemical equation with symbols for the following reactions.
(i) Solution of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
Answer:
The above equation may be represented by following chemical equation.
BaCl₂(aq) + Na₂SO₄(aq) → BaSO₄(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Answer:
The above equation may be represented by following chemical equation.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(l) + H₂O(l)
Monday, October 7, 2019
11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Alcohols
Friday, October 4, 2019
3. Atoms and Molecules IX Chapter 3
Tuesday, July 9, 2019
हमारे आस पास के पदार्थ
NCERT
पदार्थ के भौतिक स्वरूप
- पदार्थ के कणों के बीच रिक्त स्थान होता है।
- पदार्थ के कण निरंतर गतिशील होते है।
- पदार्थ के कण एक दुसरे को आकर्षित करते है।
पदार्थ की अवस्थाएँ
ठोस के कणों की गतिज ऊर्जा सबसे कम होता है।
द्रव्य के कणों की गतिज ऊर्जा ठोस के अपेक्षा अधिक लेकिन गैस के अपेक्षा कम होता है।
गैस के कणों की गतिज ऊर्जा सबसे अधिक होता है।
(b) निम्नलिखित पर टिप्पणी कीजिए
उत्तर-
दृढता
वैसे पदार्थ जिसका आकार एवं आयतन निश्चित होता है, जिसमें कण एक दुसरे बहुत नजदीक होते है। इसमें वाह्य बल लगाने पर टूट सकते है लेकिन अपना आकार नही बदलता हो दृढ होते है। पदार्थ के इस गुण को दृढता कहा जाता है। ठोस में ऐसा गुण पाया जाता है।
संपीड्यता
पदार्थ का वह गुण जिसके कारण पदार्थ के अत्यधिक आयतन को एक कम आयतन वाले वर्तन में संपीडित किया जा सकता है, पदार्थ के इस गुण को ही संपीड्यता कहा जाता है।
तरलता
पदार्थ का वह गुण जिसके कारण वह अपना आकार असानी से बदलता है तरलता कहलाता है। द्रव्य में तरलता का गुण पाया जाता है।
बर्तन में गैस का भरना
गैस के कणों की गति अनियमित एवं अत्यधिक तिव्र होती है। इस अनियमित गति के कारण इसके कण बर्तन के दीवारों से से टकराते है जिसके कारण गैस का दबाव बनता है।
गतिज ऊर्जा
ठोस में कणों की गतिज ऊर्जा सबसे कम, द्रव्य में ठोस से ज्यदा एवं गैस से कम जबकि गैस में सबसे अधिक होता है।
Recently Added
Available Educational Materials
-
"दो समरूप त्रिभुजों के क्षेत्रफलों का अनुपात इनकी संगत भुजाओं के अनुपात के वर्ग के बराबर होता है"। दियाः- दो त्रिभुज क्रमशः ...
-
Slope of a Line A line in a coordinate plane forms two angles with the x-axis, which are supplementary. The angle (say) θ made by the li...
-
Electric Generator Uses and Working Principle Based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction, the experiments studied above generate i...
-
Theorem 6.6 Statement "The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their correspondin...
-
Speed The rate of change of distance per unit time of a moving body is called speed. Speed = distance/time The SI unit of speed is metre...
-
Conservation of Linear Momentum Momentum The product of mass and velocity of a moving body is said to be momentum. It...
-
Chalcolithic Period • The end of the Neolithic period saw the use of metals of which copper was the fi rst. A culture based on the use of ...
-
Chapter 9 Class X Exercise 9.1 Q.No. 1 A circus artist is climbing a 20 m long rope, which is tightly stretched and tied from the...
-
Consider about a circular path of radius r. A body moves from A to B with uniform speed v in time t. The body subtends an angle 𝜃 at the c...
-
Class X Probability Exercise 15.1 Q.No. 1. Complete the following statements: (i) Probability of an event E + Probability of the ev...