Alphabet Reasoning
Type I: Word Formation From Letters of Another Word
In this type, you have to form words from specific letters of a given word. Next, you need to answer questions based on the new word/words formed. Below is an example.
Example Question 1: If it is possible to make a meaningful word with the fourth, the seventh, the eighth and the twelfth letters of the word “QUANTITATIVE”, which of the following will be the second letter of that word from the left end? If no such word can be made give ‘X’ as the answer and, if more than one such word can be made, give ‘M’ as the answer.
a) E b) M c) A d) X
Solution:
The given word is,
| Q | U | A | N | T | I | T | A | T | I | V | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
Fourth letter in the word is – N
Seventh letter is – T
Eighth letter is – A
And twelfth letter is – E
The meaningful word you can form using the above letters is NEAT.
(Here, we can make only one word). So, the second letter from the left end is E.
Hence, the answer is Option a) E.
Type II: Letter Series
In this type, you have to find missing letters in a series. Let us see an example.
Example Question 2: What will come in the place of (?) in the following letter series?
EG, HJ, KM, NP, ?
Solution:
The letters in the series are formed by using the logic,
G is the second letter from E.
The second term (‘HJ’) starts with the successive letter of G, i.e., H.
Below diagram will help you to understand the logic behind the series better.
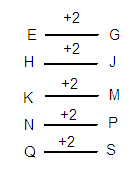
So the next letter in the series is QS. (Q is the next successive letter of P and S is the second letter from Q).
Type III: Identifying Letters That Match Given Conditions
In this type, you have to identify letters based on certain conditions given in the question. Here is an example.
Example Question 3: How many pairs of letters are there in the word “QUANTITATIVE” which have as many letters between them as in the English alphabet series?
Solution:
In the word, QUANTITATIVE you have to check for the pairs of letters that are in alphabet series.
In real alphabet series, the letters T and V have only one letter U between them.
In the word ‘QUANTITATIVE’ the letters T and V have only one letter I between them.
Therefore, TV is one such pair.
The other pair is AE. In the alphabet series, we have 3 letters between A and E., i.e., A, B, C, D and E.
Similarly, in the given word also, there are three letters between A and E.
Below diagram will help you to understand the solution better.

Hence, we have two such pair of letters (TV and AE).
Type IV: Arranging Words in Alphabetic Order
This type is the easiest of all. You have to arrange given words in alphabetical order and answer the corresponding questions.
Example Question 4: Arrange the following five words in alphabetical order as per dictionary then find which of the following word will come at the third place?
1) Music
2) Modern
3) Mobile
4) Manifest
5) Magic
Solution:
First, we have to arrange the words in dictionary (alphabetical) order.
First, check the first letter of the given words,
| Words | Letters |
|---|---|
| Music | M |
| Modern | M |
| Mobile | M |
| Manifest | M |
| Magic | M |
Here all the words start with the letter M. Therefore we have to move to the second letter to arrange in order.
| Words | Letters |
|---|---|
| Music | U |
| Modern | O |
| Mobile | O |
| Manifest | A |
| Magic | A |
Based on the second letter, the words can be arranged as,
Manifest
Magic
Modern
Mobile
Music
Here, the second letter of the words ‘Manifest’ and ‘Magic’ are same. Similarly, for ‘Modern’ and ‘Mobile’ the second letters are the same. In order, to find the proper arrangement we have to check with the third letter of these words.
| Words | Letters |
|---|---|
| Manifest | N |
| Magic | G |
| Modern | D |
| Mobile | B |
Now the arrangement is,
Magic
Manifest
Mobile
Modern
Music
The word that comes at the third place is ‘Mobile’.
Type V: Arrangement of Letters and Interpretation
In this type, you will find conditions based on which you have to arrange letters. Then you have to answer the questions based on the new arrangement. Below example will help you to understand clearly. (There are 3 sub questions to the below one.)
Example Question 5: Directions (i- iii) Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
Write the first 10 letters of above alphabets in reverse order, followed by next 6 letters, followed by remaining 10 letters in reverse order.
(i). Which letter will be the thirteenth to the right of the third letter from right?
Solution to sub-question (i):
First, we have to arrange the letters based on the condition given.
Step 1 : Arrange first 10 letters in reverse order.
JIHGFEDCBA
Step 2: Next 6 letters should be followed as it is,
JIHGFEDCBAKLMNOP
Step 3: The remaining 10 letters should be reversed
JIHGFEDCBAKLMNOPZYXWVUTSRQ
Now, we have arranged the alphabets according to the question.
Next, we have to find the thirteenth letter right to the third letter from your right. You can find it using the diagram(i) shown below.

The required letter is K.
(ii). Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to the group?
a) FDA b) LNZ c) PYV d) OZX e) WUR
Solution to sub question (ii):
In the arrangement we just created. (refer to diagram in sub-question (i))
Consider the first option ‘FDA. Here, D is the second letter from F and A is the third letter from D. The same logic is used to form all the terms except option d) OZX.
Below diagram will help you to understand the logic better.

(iii). How many letters are there in between letters F and O in the sequence?
Solution to sub-question (iii):
Based on our arrangement diagram (refer to the diagram in sub-question (i)), the letters in the sequence are,
| F | E | D | C | B | A | K | L | M | N | O |
The number of letters between F and O is 9.