Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Class XII
Subject : Chemistry
Alcohols
Alcohols are compounds in which a hydroxyl(-OH) group attached to the saturated carbon atom.
General formula of alcohol - R-OH
The hydroxyl group is the functional group of alcohols.
Alcohols containing one hydroxyl are called Monohydric Alcohols.
Alcohols with two, three, or more hydroxyl groups are known as Dihydric Alcohols, Trihydric Alcohols, and Polyhydric Alcohols respectively.
For example,
Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Alcohols
Monohydric alcohols are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary depending upon whether the -OH group is attached to primary, secondary or a tertiary carbon.
Structure
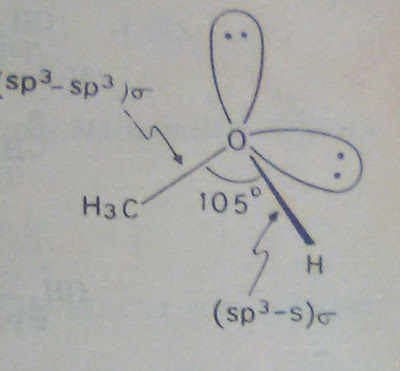
Consider about the structure of Methyl Alcohol (CH₃OH). In methyl alcohol both oxygen and carbon are sp³ hybridized. Two of the sp³ orbitals of oxygen are completely filled and cannot take part in bond formation.
The C-O bond methyl alcohol is formed by overlap of an sp³ orbital of carbon and an sp³ orbital of oxygen. The O-H bond is formed by overlap of an sp³ orbital of oxygen and s orbital of hydrogen. The C-O-H bond angle is 105⁰. It is less than the normal tetrahedral angle. This is because the two completely filled sp³ orbitals of oxygen repel each other. This result in reduction of the bond angle.
Structure of Methyl Alcohol is given below
Continue ................